Cyberintegrator
Project Page: https://opensource.ncsa.illinois.edu/projects/CBI
Repository: https://opensource.ncsa.illinois.edu/stash/scm/cbi/cyberintegrator-3.git
Documentation: Web | PDF
Bug Reporting: Jira
License: NCSA Open Source
Status: Archived
This project is replaced by http://opensource.ncsa.illinois.edu/projects/WOLF
CyberIntegrator is an exploratory workflow system emphasizing distributed execution of arbitrary software, data reproducibility, and ease of use. CyberIntegrator addresses the problem of analytical reproducibility in an era where nearly all research/practice involves software and digital data, and where both software and digital data can change over time thus preventing the reproduction of results. The projects using Cyberintegrator have developed interactive Web applications with easy-to-use interfaces supported by sophisticated back-end analyses and models for specific science, industry, and policy domains.
DataWolf (formerly Cyberintegrator) is a user friendly editor to several middleware software components that (1) enable users to easily include tools and data sets into a software/data unifying environment, (2) annotate data, tools and workflows with metadata, (3) visualize data and metadata, (4) share data and tools using local and remote context repository, (5) execute step-by-step workflows during scientific explorations, and (6) gather provenance information about tool executions and data creations.
The middleware software components are:
- multiple plug-in codes called executors for running external tools, Matlab scripts and Java codes,
- Tupelo data and metadata archiving system based on the Resource Description Framework (RDF) metadata model and
- portal systems, currently Cyber-collaboratory based on Liferay portal technology.
Cyberintegrator is a highly interactive environment to support and address the many needs of scientific processes. It was created at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The ultimate goal is to support scientific discoveries and to provide means for conducting research more efficiently. Development evolved from the Environmental Cyberinfrastructure Demonstrator (ECID) project to support environmental engineering, science and hydrology research and continues with the help of Technology Research Education and Commercialization Center (TRECC).
The current implementation enables users:
- to browse registries of data, software tools and computational resources,
- to create meta-workflows by example (step by step execution),
- to re-use and re-purpose meta-workflows,
- to execute meta-workflows locally or remotely,
- to incorporate heterogeneous code executors and tools, and link them transparently,
- to provide recommendations about workflow completion,
- to search for data, tools and resources in registries, and
- to support processing of streaming data and large size, out-of-core, data.
The Cyberintegrator editor is built on top of the Eclipse Rich Client Platform (RCP) to achieve its full functionality of re-configurable user interface and plug-and-play architecture critical for easy deployment of the Cyberintegrator application.
Source code is available from our git repository at https://opensource.ncsa.illinois.edu/stash/scm/cbi/cyberintegrator-3.git and can be checked out as follows:
git clone https://opensource.ncsa.illinois.edu/stash/scm/cbi/cyberintegrator-3.git
If you wish to contribute code to the project please contact kooper@illinois.edu.We would like to acknowledge multiple funding agencies for the support including NCSA, NSF, NASA, NARA and TRECC. The main creators of Cyberintegrator are Rob Kooper, Luigi Marini and Peter Bajcsy with support from Barbara Minsker, Jim Myers, and Tim Nee.
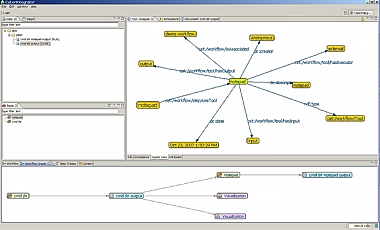
The workflow graph of the directory listing followed by the Notepad tool execution.